Celiac disease, a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, primarily affects the small intestine. Over time, if left unmanaged, it can lead to severe complications, including an increased risk of other digestive cancers. This risk makes it critical for individuals with celiac disease to understand how to manage their condition effectively and what steps they can take to protect their overall digestive health. In this blog, we’ll explore the connection between celiac disease and digestive cancers, discuss the importance of chronic conditions care, and emphasize the role of in-home care in managing these risks.
Understanding Celiac Disease and Its Complications
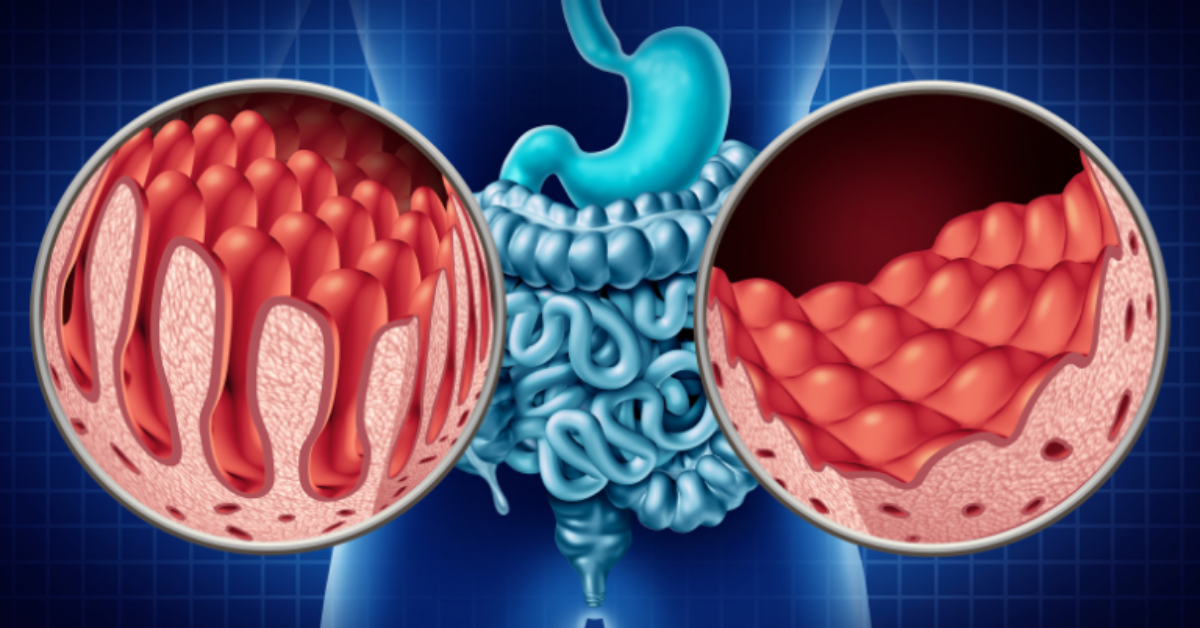
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye—triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage can interfere with nutrient absorption, leading to a range of symptoms such as diarrhea, weight loss, anemia, and fatigue. For some, the symptoms are mild and easily managed, while for others, they can be debilitating.
The chronic inflammation caused by untreated celiac disease can lead to serious complications over time, including the development of other autoimmune disorders and an increased risk of digestive cancers, such as small intestine cancer, esophageal cancer, and colon cancer.
The Connection Between Celiac Disease and Digestive Cancers
The link between celiac disease and an increased risk of certain digestive cancers has been well-documented in medical literature. Chronic inflammation in the small intestine, a hallmark of untreated or poorly managed celiac disease, creates an environment that can lead to cellular changes and, eventually, cancer.
- Small Intestinal Adenocarcinoma: The risk of developing small intestinal adenocarcinoma is higher in individuals with celiac disease, particularly if the condition is undiagnosed or untreated for a long period. This type of cancer affects the small intestine, the primary site of damage in celiac disease.
- Esophageal Cancer: Chronic inflammation and the potential for esophageal damage can also increase the risk of esophageal cancer in those with celiac disease. The inflammation may lead to changes in the cells lining the esophagus, potentially resulting in cancer.
- Colon Cancer: Although the risk is not as high as that for small intestinal or esophageal cancers, studies suggest that individuals with celiac disease may also have an increased risk of colon cancer, particularly if they do not adhere to a strict gluten-free diet.
Importance of Managing Celiac Disease to Reduce Cancer Risk
For individuals with celiac disease, managing the condition is crucial not only to alleviate symptoms but also to reduce the risk of serious complications, including digestive cancers. The most effective way to manage celiac disease is through strict adherence to a gluten-free diet, which helps to heal the intestinal lining and reduce inflammation. However, managing celiac disease requires more than just dietary changes—it often necessitates a comprehensive approach to health, particularly for those who may be at increased risk for other chronic conditions.
Chronic Conditions Care and the Role of In-Home Care
Chronic conditions care is essential for individuals with celiac disease, especially when they are managing additional health challenges. Celiac disease can complicate the management of other chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis, making a coordinated approach to care critical. This is where chronic conditions home care, particularly in-home care, becomes invaluable.
Personalized In-Home Care for Chronic Conditions
In-home care provides personalized support tailored to the unique needs of individuals with chronic conditions like celiac disease. Caregivers can assist with meal planning and preparation to ensure that all meals are gluten-free while also catering to the dietary needs of other conditions, such as low-sodium diets for heart disease or carbohydrate control for diabetes.
For those with more severe symptoms or additional chronic conditions, 24-hour in-home care may be necessary. This level of care ensures that individuals receive continuous support, from managing medications to monitoring for any signs of complications, such as symptoms that could indicate an increased risk of cancer.
Monitoring and Managing Symptoms
One of the critical aspects of managing celiac disease and reducing the risk of complications like digestive cancers is regular monitoring of symptoms. In-home caregivers can play a pivotal role in this by keeping track of any changes in health status, ensuring that the individual adheres to their gluten-free diet, and watching for any signs of nutritional deficiencies or other health issues that may arise.
For example, chronic fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or changes in bowel habits could be signs that something is amiss, potentially indicating a need for further medical evaluation. In-home caregivers can help facilitate timely medical appointments and ensure that any necessary tests are conducted promptly.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with celiac disease and the associated risks of other chronic conditions or cancers can be emotionally taxing. In-home care providers can offer not just physical assistance but also emotional support, helping individuals cope with the stress and anxiety that often accompany chronic illness. This holistic approach to care is essential for maintaining overall well-being and quality of life.
The Benefits of 24-Hour Home Care
For individuals with advanced celiac disease or those managing multiple chronic conditions, 24-hour home care offers numerous benefits. Around-the-clock care ensures that any potential health issues are addressed immediately, which is particularly important for those at risk of developing digestive cancers. Caregivers can provide continuous monitoring, assist with mobility and daily activities, and offer companionship, all of which contribute to better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Preventive Measures and Regular Screening
Preventive measures are key to reducing the risk of digestive cancers in individuals with celiac disease. This includes not only adhering to a gluten-free diet but also undergoing regular medical screenings as recommended by healthcare providers. For those with a higher risk of cancer, such as individuals with a long history of untreated celiac disease, regular endoscopies and other relevant tests may be necessary to monitor the health of the digestive tract.
In-home care providers can play a significant role in ensuring that individuals follow through with these preventive measures, from scheduling and accompanying them to medical appointments to helping them understand the importance of regular screenings.
Conclusion: Comprehensive In-Home Care for Managing Celiac Disease and Cancer Risk
Living with celiac disease requires diligent management to prevent complications and reduce the risk of associated digestive cancers. Chronic conditions care, particularly in the form of personalized in-home care, provides the support needed to manage this complex condition effectively. Whether it’s through regular monitoring, personalized dietary planning, or providing emotional support, in-home care services play a significant role in helping individuals with celiac disease maintain their health and quality of life.
For those at higher risk or managing multiple chronic conditions, 24-hour in-home care offers continuous, comprehensive support that can make a significant difference in preventing complications and ensuring overall well-being. If you or a loved one is living with celiac disease, consider the benefits of in-home care as part of your strategy for managing the condition and protecting your digestive health.
By staying informed, following preventive measures, and receiving the appropriate level of care, individuals with celiac disease can lead healthy, fulfilling lives while minimizing the risks of developing serious complications, including digestive cancers.